Levomilnacipran is a selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) available by the brand name of Fetzima. It is indicated in the treatment of patients with major depression and fibromyalgia.
Levomilnacipran (Fetzima) is one of the few drugs that treats the psychiatric component of long-standing painful conditions. Most patients with chronic conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis also develop low mood and depression. Such patients perform well when treated with SNRIs like Levomilnacaprin (in addition to the treatment of their underlying disorder which should be the primary objective.
Levomilnacipran (Fetzima) MOA: How it works?
Levomilnacipran is an active form (enantiomer) of Milnacaprin. It acts by increasing the levels of serotonin in the brain which helps in alleviating the symptoms of depression and anxiety. It also increases the levels of norepinephrine in the brain which inhibits the pain signals at the level of the spinal cord.
The combined effect on serotonin and norepinephrine is the reason behind the drugs efficacy in painful conditions and depression such as fibromyalgia.
Levomilnacipran Dosage and Formulation:
Levomilnacipran is available by the brand name of Fetzima. It is registered by Pierre Fabre Medicament S.A.S. It is available as an extended-release formulation and is administered as 20 mg orally once a day. The dose may be increased after two days to 40 mg once a day. Further doses may be increased in increments of 20 mg every two to four weeks up to a maximum daily dose of 120 mg daily.
Patients with moderate kidney impairment such as those with a creatinine clearance between 30 and 39 mL/minute should not exceed a dose of 80 mg daily. Patients with severe impairment (creatinine clearing 15 to 29mL/minute) should not exceed 40 mg per day. Patients with end-stage renal disease should not be advised the drug. It can be used in liver disease.
Fetzima is not indicated for use in children and pregnant females
It is important to take the drug as a whole without crushing, chewing, or breaking the tablet. It can be taken with or without food. However, in patients with gastric upset, it is best to take it after a meal with a glass of water or milk.
Levomilnacipran (Fetzima) Side effects and Safety Concerns:
Levomilnacipran should not be prescribed to patients who have end-stage renal disease and those with a seizure disorder. It should also be avoided in patients with angle closure, patients with uncontrolled hypertension, and other cardiovascular conditions that could be made worse by high blood pressure.
Dose-dependent effects of the drug on urinary urgency may occur in patients who have had a history of urinary obstruction. It can also increase the risk of bleeding and should be avoided in patients who are on blood thinners like warfarin, apixaban, dabigatran, and rivaroxaban.
It has been associated with fractures, however, data in this regard is limited. It can cause a life-threatening condition called serotonin syndrome. These patients may develop high grade fever, become drowsy, develop hypotension or hypertension, and seizures.
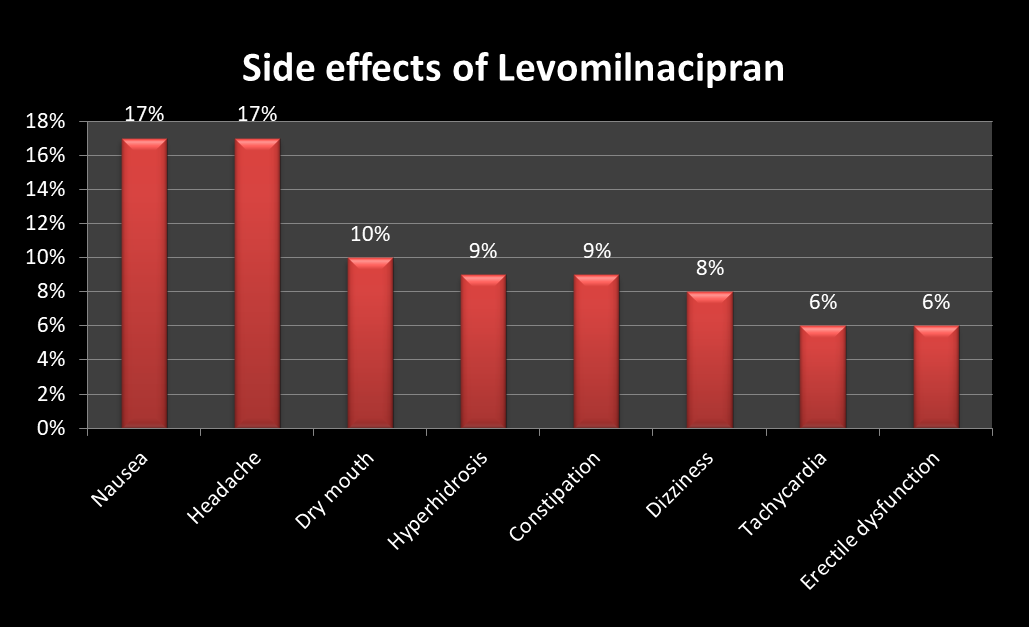
Other less severe side effects of the Levomilnacipran include Nausea, constipation, headache, dry mouth, excessive sweating, dizziness, palpitation, increased heart rate, and sexual dysfunction.
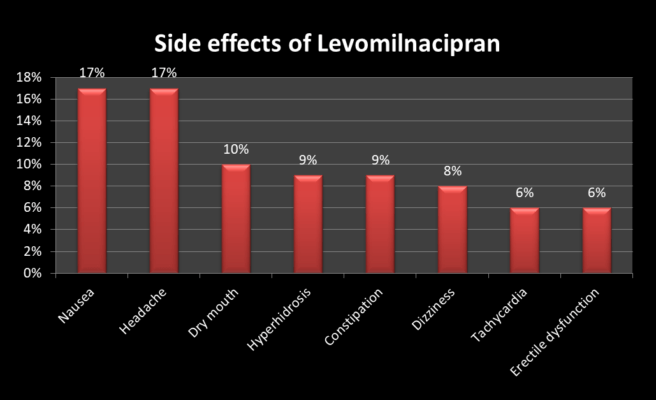
The gastrointestinal side effects of the drug can be minimized when it is taken after a meal. Furthermore, the likelihood of developing side effects and the intensity of the disease is associated with the frequency and dose of the drug. In low dose, side effects may be minimal. In addition, side effects are more likely during the first few weeks of treatment initiation. With time the body gets used to the drug and adjusts to the side effects.
In practice, the incidence of urinary hesitancy and erectile dysfunction was seen more often when the drug was administered in doses exceeding 40 mg per day.
The Cardiovascular side effects of Levomilnacipran (Fitzima):
Cardiovascular side effects are common with most SNRIs bacause of the effect of these drugs on nor-epinephrine.

Heart rate:
- Levomilnacipran causes tachycardia. The effect was demonstrated in one trial when the drug caused an increase in the heart rate by 7.4 beats/minute compared to the placebo which reduced it by 0.3 beats pr minute on an average. This effect persists with prolonged treatment.
Blood pressure:
- An increase in blood pressure commonly occurs in the treatment arm compared to placebo. An average rise in blood pressure of 3.0 and 3.2 mmHg in the systolic and diastolic has been observed respectively compared to a reduction of 0.4 mmHg with placebo treatment.
- Although, the effect is not substantial, patients who have pre-existing hypertension need to monitor their blood pressure and adjust their medications appropriately.
QTc interval prolongation:
- Levomilnacipran does not cause QTc prolongation when administered in doses up to 300 mg per day that is almost 2.5 times the maximum recommended dose.
The effect of Levomilnacipran (Fitzima) on body weight:
Levomilnacipran, like other SNRIs, does not cause a significant change in the body weight. It has been found to be weight-neutral in clinical trials.
Read: Which Antidepressant Does Not Cause Weight Gain
How to discontinue Levomilnacipran (Fitzima):
Patients must be advised to taper the drug slowly and avoid abruptly stopping the drug. It is best to reduced the dose by 20 mg at weekly intervals until 20 mg per day dose is reached. patients are then maintained on 20 mg per day for two weeks and then discontinued or switched to alternate day treatment first and then discontinue the treatment.
Slow tapering of the drug results in a decreased chance of relapse and minimal withdrawal symptoms especially body pains and anxiety.
Read: Serotonin Modulators; Nefazodone, Trazodone, Vilazodone, Vortioxetine