Semaglutide is a GLP-1 analog that is 94% identical to the endogenous human GLP-1. It is available in the form of injections as Ozempic and Wegovy and as oral medicine by the brand name of Rybelsus.
It is used to treat patients with Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 as an adjunct to diet and exercise. Recently, it has also got approval for weight loss in obese and overweight individuals especially those who have underlying metabolic syndrome or diabetes mellitus type 2.
It has also been found to significantly reduce the major cardiovascular events including cardiovascular deaths, non-fatal myocardial infarction, and non-fatal stroke in diabetic patients.
It has also been found to be an effective treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and NASH. It significantly reduces the inflammatory markers in patients with NASH.
Oral Semaglutide: Rybelsus (Taken Daily)
Injectable Semaglutide: Ozempic & Wegovy (Administered Weekly)
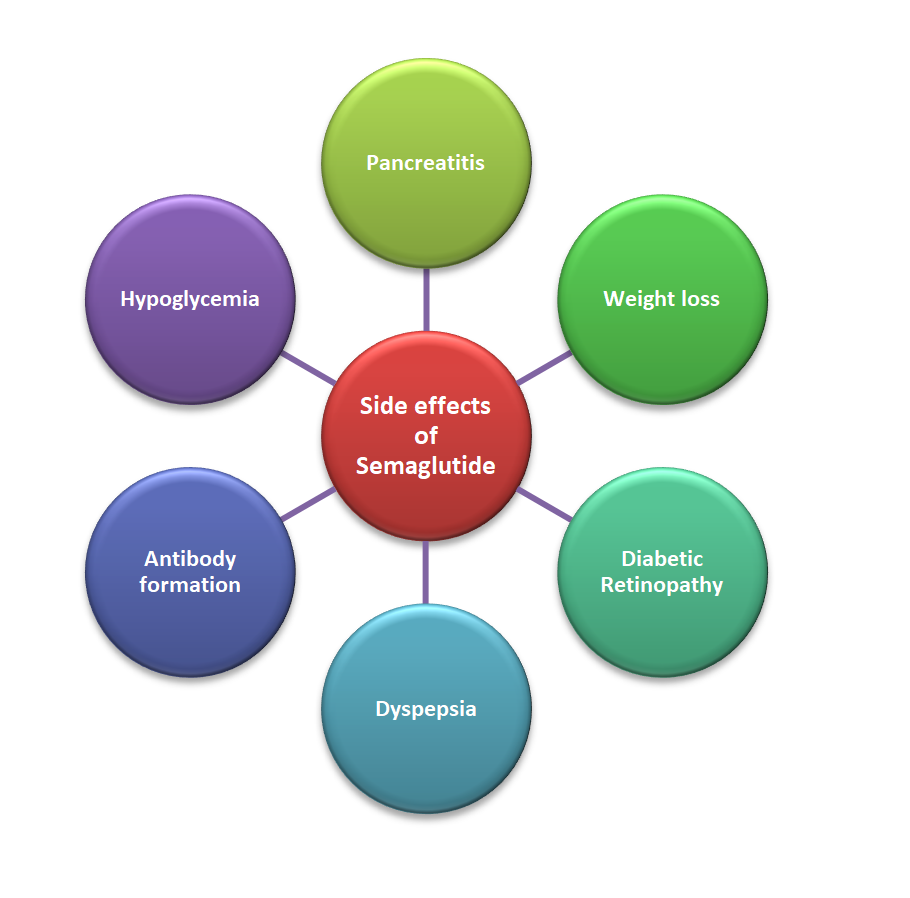
What are the Side effects of Oral and Injection Semaglutide?
Before discussing the side effects of Semaglutide, it is important to know that some diabetic patients should not use Semaglutide at all. It is totally contraindicated in patients who are allergic to the drug or any component of the formulation.
Avoid in patients with Medullary Thyroid Carcinomas:
Its use should be avoided in patients with a family or personal history of medullary thyroid carcinoma and those with a history of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 (MEN II). Patients who are at high risk should have serum calcitonin measured before treatment initiation.
Avoid in patients with major organ dysfunction and pregnancy:
It should not be given to pregnant females and to lactating women. It should be used with caution in patients with a history of pancreatitis or hepatobiliary disease including those with active symptomatic gallstones. It should be avoided in advanced liver and kidney disease or acutely decompensated liver or hepatic diseases.
Don’t use in patients undergoing bariatric surgery:
It should be used with extreme caution in patients undergoing bariatric surgery since it may be associated with gastrointestinal upset and may lead to dehydration. Bariatric surgery may also increase the endogenous GLP-1 levels. Exogenous GLP-1 administration including either oral Semaglutide (Rybelsus) or injectable Semaglutide (Ozempic) may result in acute pancreatitis in these patients.
Ocular Side effects of Semaglutide and effect on diabetic retinopathy:
Semaglutide has been associated with a worsening of pre-existing diabetic retinopathy and patients with a baseline of moderate to severe diabetic retinopathy. It has been reported to cause blindness, vitreous hemorrhage, and a worsening of diabetic retinopathy.
Some experts suggest that the worsening of these symptoms is secondary to the glucose shift and improvement in glycemic control. Similar findings have also been documented in patients who have undergone bariatric surgery.
Gastrointestinal Side effects of Semaglutide (Rybelsus and Ozempic):
All GLP-1 analog (liraglutide, Semaglutide, Dulaglutide) and drugs that increase the half-life of GLP-1 analogs like DPP-IV inhibitors (Sitagliptin and Vildagliptin) can cause stomach fullness and delay gastric emptying.
Semaglutide has been associated with gastrointestinal side effects like nausea, vomiting, post-meal bloating, early satiety or the feeling of being full all the time, diarrhea, and constipation. In fact, the most common side effects of oral and injectable Semaglutide are related to the gastrointestinal tract.
It has been associated with a non-specific elevation of pancreatic enzymes. However, it may cause pancreatitis in high-risk patients and should be avoided in patients with recurrent pancreatitis or those with a history of pancreatitis.
Hypoglycemic side effects of Semaglutide:
It causes the glucose-dependent release of insulin and suppresses glucagon in a glucose-dependent manner. However, when given in combination with other anti-diabetic medications or insulin, it can cause hypoglycemia. Patients may report dizziness, vertigo, sweating, palpitations, and hunger.
Other Side effects of Semaglutide:
In clinical trials, 1% of the patients were noted to develop antibodies against the drug, however, the significance of these antibodies is not known. It is not known whether these antibodies can have any effect on the drug’s efficacy or not is yet to be determined.
It can cause a non-significant increase in the heart rate, however, it is considered safe in patients with heart diseases and reduces cardiovascular mortality in diabetic patients.