Lorazepam vs Clonazepam is a comparison of the two commonly used benzodiazepines. Although, both can be used for sleep, seizures, anxiety, and panic disorders, there are slight differences.
Lorazepam Vs Clonazepam Introduction:
Lorazepam (Ativan) and clonazepam (Klonopin) are two medications used in the treatment of depression and anxiety disorders. Both of them belong to the class of drugs known as benzodiazepines.
These drugs work by binding to GABA (Gamma-aminobutyric acid) receptors in the brain. They enhance the effects of GABA, a neurotransmitter that inhibits the activity of the brain. Excessive brain activity is believed to cause anxiety disorders.
Lorazepam and clonazepam, both are considered intermediate-acting benzodiazepines.
What are the main differences between Lorazepam and Clonazepam?
- Clonazepam is mainly used to treat panic disorders and seizures. It has a half-life of 30 to 40 hours and stays in the blood for relatively long periods.
- Lorazepam is used to treat anxiety and seizures.it is also effective in the treatment of insomnia and panic attacks. It can be used in combination with other drugs to treat nausea and vomiting caused due to chemotherapy. The injectable form of lorazepam can also be used for anesthesia in certain surgical procedures. Lorazepam has a half-life of 20 hours in the body.
- Both are FDA-approved drugs for the treatment of seizures, clonazepam is used in the treatment of akinetic and myoclonic seizures while lorazepam treats a severe form of seizure known as status epilepticus.
Clonazepam is used to treat akinetic and myoclonic seizures while Lorazepam is used to treat patients in status epilepticus
Mode of action of Lorazepam vs Clonazepam:
Both drugs act by binding to the benzodiazepine receptors in different sites in the central nervous system (CNS). This binding results in increased inhibitory effects of GABA which increases the flow of chloride ions into cells thereby causing hyperpolarization and stabilization of the plasma membrane.
By enhancing the neuro-inhibitory activity of GABA these drugs inhibit neuronal activity and facilitate in decreasing any excessive electrical nerve activity.
Absorption of Lorazepam vs Clonazepam:
- Lorazepam is readily absorbed when given orally. It has an absolute 90% bioavailability. The intramuscularly administered dose is completely absorbed within 15-30 minutes. Orally administered dose attains maximum concentration in 2 hours.
- Clonazepam is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, attaining peak concentrations within 1-4 hours. Its absolute bioavailability is approximately 90%.
Comparison of Lorazepam and Clonazepam (Ativan vs Klonopin):
Lorazepam | Clonazepam | |
| Brand Names | Ativan | Klonopin |
| Onset of action | Sedation occurs in 2 – 3 minutes with IV administration and 20 to 30 minutes after IM administration. Anti-seizure activity is seen in about 10 minutes | 20 to 40 minutes |
| Duration of action | 6 – 8 hours | 12 hours or less |
| Bioavailability | 90% | 90% |
| Half-life elimination | 12 – 18 hours | 17 – 60 hours |
| Peak serum concentration | 2 hours | 1 to 4 hours |
Efficacy of Lorazepam vs Clonazepam in Anxiety Disorder:
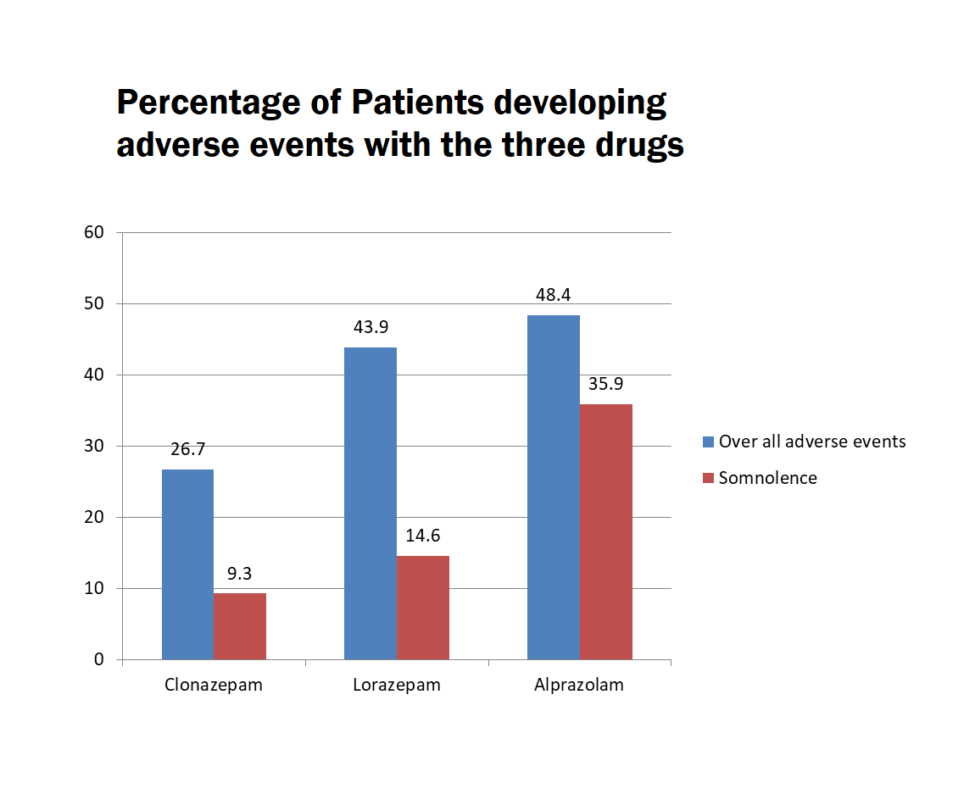
In a multicenter study, both clonazepam and lorazepam were found to be equally effective in the treatment of anxiety disorders. No significant differences were found between the two drugs regarding improvements in anxiety and sleep scores. However, the study found that there were fewer side effects associated with clonazepam rather than lorazepam [Ref].
Efficacy of Lorazepam vs Clonazepam in Seizures:
In another study in the comparison of both drugs was done for status epilepticus. Although lorazepam is approved and widely used for status epilepticus, clonazepam was also found to be useful. Patients in the Lorazepam group had a greater improvement in their EEG from baseline, however, clinical improvement was more in patients treated with clonazepam [Ref].
Efficacy of Lorazepam vs Clonazepam in Mania:
Mania is a disorder in which the patient becomes aggressive, euphoric, delusional, hyperactive, and have intense moods. It is usually present in patients with bipolar depression that has episodes of depression as well as mania.
Different drugs like lithium, valproic acid, and anti-epileptics are being used to treat patients with mania. Lorazepam and Clonazepam were compared in a head to head trial in patients with mania. It was found that lorazepam and not clonazepam resulted in significant improvement in the symptoms of patients with mania [Ref].
Dosages of Lorazepam vs Clonazepam:
Clonazepam
The dose is prescribed according to the patient’s needs
- For seizures, the initial adult dose is 1.5 mg daily in 3 divided doses. Dosage can be increased by 0.5 or 1 mg daily for every three days until seizures are controlled
- The maximum dose of clonazepam for seizures is 20 mg daily
- The initial daily dose for panic disorders is 0.25 mg twice daily
Lorazepam
- The usual dose is 2-6 mg every 8-12 hours for treating anxiety.
- A daily dose of 2-4mg is given for the treatment of insomnia.
Side effects of Lorazepam vs Clonazepam:
Lorazepam and clonazepam have almost similar side effects, these drugs mainly affect the central nervous system (CNS). These drugs cause drowsiness, impaired thinking, dizziness, memory loss, and problems in coordination.
Clonazepam causes less impairment of memory because of its low lipid solubility
Side Effects of Clonazepam:
The most common side effects of clonazepam are sedation that is reported in almost half of the patients. Other common side effects include:
- Depression
- Weakness
- Loss of orientation
- Sleep disturbance
- Fatigue and confusion
- Amnesia
- Changes in sexual desire
Other serious side effects include:
- Fainting
- Liver enlargement
- Respiratory distress
Symptoms that occur if the drug is suddenly stopped:
- Tachycardia
- Hypotension (low blood pressure)
- Blood disorders
Side effects of Lorazepam:
The most common side effects associated with lorazepam include:
- Weakness
- Dizziness
- Sedation
- Light-headedness
Other side effects include:
- Headaches
- Sleep disturbance
- Depression
- Amnesia
Serious side effects include:
- Suicidal ideation
- Respiratory depression
Warnings and Precautions:
Like all benzodiazepines, lorazepam and clonazepam can cause physical dependence. Sudden stopping the therapy after few months of daily intake may cause the feeling of loss of self-worth, insomnia, sweating, tremors, vomiting, and muscle cramping
Drug interactions of Lorazepam vs Clonazepam:
Clonazepam (Klonopin) and lorazepam (Ativan) can interact with other drugs that cause similar effects. Taking opioids and narcotics can increase the side effects like sedation, drowsiness, dizziness, slow breathing and can even cause coma.
Drug interactions of Lorazepam (Ativan)
Benzodiazepines like lorazepam produce increased central nervous system (CNS) depressing effects when administered with other CNS depressants such as antipsychotics, hypnotics, anxiolytics, antidepressants, sedative antihistamines, and alcohol.
Drug interactions of clonazepam (klonopin)
The CNS depressing action of clonazepam may be potentiated by barbiturates, antianxiety agents, phenothiazines, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, butyrophenone, and anticonvulsant drugs.
It is important to provide a list of all the medicines to your healthcare provider when on Klonopin treatment. Clonazepam can interfere with some medicines and can affect how well they work.
Clonazepam and lorazepam both are processed in the liver, some other drugs that are processed in the same way must b avoided. Liver enzyme inhibitors like ketoconazole, erythromycin, and ritonavir can increase the level of benzodiazepines in the body resulting in increased side effects. Liver enzyme inducers like phenytoin and carbamazepine decrease the level of benzodiazepines in the body.
Warnings and precautions:
- Taking benzodiazepines with opioids should be avoided. This can cause a greater risk of respiratory depression, coma, and death.
- Benzodiazepines are considered schedule IV drugs by DEA that’s why they are only recommended for short-term use only
Clonazepam vs lorazepam during pregnancy
Klonopin and Ativan both are listed in Pregnancy category D. They should not be taken during pregnancy. Both drugs should be avoided during pregnancy and lactation. They increase the risk of birth defects therefore you must tell your healthcare provider about these medications before planning a pregnancy.
Clonazepam and lorazepam with alcohol
Benzodiazepines like clonazepam and lorazepam are not recommended while drinking alcohol. This might increase the risk of side effects like sedation, drowsiness, and fainting. Drinking alcohol can also cause overdose and result in respiratory depression, coma, and even death.
In Summary:
Both drugs are effective for treating conditions like anxiety and seizure disorders. These may be prescribed one over the other depending upon the medical history of the patient. Clonazepam and lorazepam both work in identical ways.
Both can treat anxiety disorders and seizures but are different in how long they work. Ativan (lorazepam) can also be used as a premedication for anesthesia while Klonopin (clonazepam) is not used for this purpose.